Adverb Meaning and Examples: A Simple Guide for Class Students
When you’re learning English, it’s essential to understand the role of different parts of speech. One of these key parts is the adverb. So, what is an adverb? In simple terms, an adverb is a word that describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
Adverbs provide extra information about how, when, where, or how much something happens. In this blog post, we’ll explore adverb meaning, examples, and how to use them in sentences.
What is an Adverb? (Adverb Meaning)
An adverb is a word that provides additional information about a verb (action), adjective (describes a noun), or even another adverb. They tell us how, when, where, why, or to what extent something is happening. Let’s explain this a bit more simply:
- How something is done (e.g., quickly, slowly, carefully).
- When something happens (e.g., now, yesterday, soon).
- Where something happens (e.g., here, there, everywhere).
- To what extent something is done (e.g., very, quite, almost).
Adverbs can also describe the frequency of an action, such as always, never, or often.
For example:
- He runs quickly. (How he runs)
- She will come soon. (When she comes)
- The book is very interesting. (To what extent it is interesting)
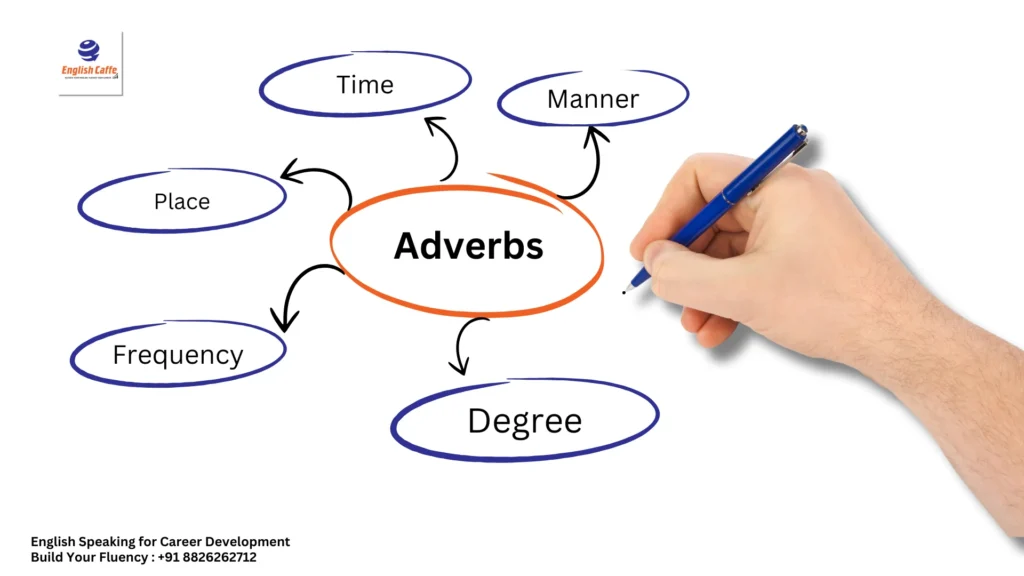
Types of Adverbs
There are several types of adverbs, and they help give us more specific information. Here are the most common ones:
Adverbs of Manner –
These adverbs describe how something is done. Most adverbs of manner end in “-ly.”
- Examples: quickly, slowly, carefully, loudly, happily
- Example sentence: She sings beautifully.
Adverbs of Time –
These adverbs tell us when something happens.
- Examples: now, later, soon, always, yesterday
- Example sentence: I will call you tomorrow.
Adverbs of Place –
These adverbs tell us where something happens.
- Examples: here, there, everywhere, anywhere
- Example sentence: They are playing outside.
Adverbs of Frequency –
These adverbs show how often something happens.
- Examples: always, never, often, sometimes
- Example sentence: He often visits his grandparents.
Adverbs of Degree –
These adverbs show how strong or intense an action, adjective, or another adverb is.
- Examples: very, quite, too, almost, enough
Example sentence: The movie was very interesting.

Examples of Adverbs in Sentences
Let’s look at some more examples to see how adverbs work in sentences:
- She runs very fast. (Adverb of degree: “very”)
- The cat is hiding somewhere. (Adverb of place: “somewhere”)
- He works hard every day. (Adverb of frequency: “every day”)
- I will visit you tomorrow. (Adverb of time: “tomorrow”)
- They play beautifully. (Adverb of manner: “beautifully”)
Notice how adverbs can modify the verb in the sentence, giving us more detail about the action.
Adverb Practice Worksheet for Class 3, 4, and 5
Part 1: Identifying Adverbs in Sentences
Read each sentence carefully and underline the adverb.
- The cat runs fast.
- He answered the question correctly.
- She is always happy.
- The children played outside yesterday.
- He can jump very high.
- The teacher speaks loudly in class.
- The dog barked loudly at the mailman.
- I saw her once during the vacation.
- The sun rises early in the morning.
- My brother plays the guitar well.
Part 2: Classifying Adverbs
Classify the adverbs in the following sentences under the correct heading. Write the appropriate number in front of the adverb.
Adverbs of Manner (How): ?
Adverbs of Time (When): ?
Adverbs of Place (Where): ?
Adverbs of Degree (How much): ?
Adverbs of Frequency (How often): ?
- He answered the questions quickly.
- She wakes up early every day.
- They live nearby.
- I am feeling very tired.
- We go to the beach always in summer.
- The dog barks loudly.
- The meeting will start soon.
- The children are playing outside.
- He was quite angry about the news.
- She is never late for school.
Part 3: Fill in the Blanks with Adverbs
Choose the right adverb from the list below to complete each sentence. Some adverbs can be used multiple times.
List of Adverbs: quickly, always, here, never, quietly, very, too, late, everywhere, today
- The boy finished his homework ______.
- I have ______ forgotten to bring my notebook.
- We are going to the park ______.
- They are ______ playing outside, even in the rain.
- The dog was barking ______ at the stranger.
- She speaks ______ when she is in class.
- He was ______ tired after the game.
- We will see you ______ at the party tonight.
- She is ______ on time for school.
- They came ______ for the meeting.
Part 4: Correct the Mistakes
Find the mistake in each sentence below. Write the sentence again correctly.
- She sings beautiful.
- He talks so louder than me.
- The teacher speaks quick in the class.
- They run very fastly in the race.
- I will never goes to the market.
- The book was too much interesting.
- She eats slowly very.
- The dog sleeps quiet.
- He works hard really.
- The children play there often.
Part 5: Make Sentences with the Given Adverbs
Write a sentence using each of the following adverbs:
- quickly
- yesterday
- outside
- always
- very
- never
- loudly
- soon
- too
- carefully
Part 6: Create Your Own Sentences
In this section, use the following words to create your own sentences with adverbs. Be sure to describe how, when, or where something happens.
- He / play / soccer / well
- The dog / bark / loudly
- She / do / homework / carefully
- They / wait / patiently
- I / eat / too / much / candy
- We / go / outside / every / weekend
- The teacher / speak / slowly / in class
- I / call / you / soon
- She / smile / brightly
- The baby / sleep / soundly
Part 7: Adverb Match
Match the sentence with the adverb that best fits. Write the letter of the correct adverb next to the sentence number.
- They go to the park _____.
a) loudly
b) often
c) outside
d) quickly - The baby is sleeping _____.
a) loudly
b) peacefully
c) too much
d) always - She answered the question _____.
a) soon
b) very
c) carefully
d) now - The teacher spoke _____.
a) everywhere
b) slowly
c) late
d) too - I will come to your house _____.
a) loudly
b) soon
c) well
d) everywhere
Part 8: True or False
Read the following statements and write True or False next to each one.
- An adverb can only modify a verb. ______
- Adverbs of degree tell us when something happens. ______
- She sings beautifully” is an example of an adverb modifying a verb. ______
- I will visit you soon” is an example of an adverb modifying an adjective. ______
- The cat runs fast” is an example of an adverb modifying a noun. ______
Why Are Adverbs Important?
Adverbs make our sentences more interesting and informative. Without them, our language would sound very plain and not as descriptive. For example, instead of saying “She walks,” you could say “She walks gracefully” or “She walks quickly,” which adds more meaning to the action.
Think of adverbs as spice to a dish. They give flavor to what you’re saying. They can make your writing clearer, more precise, and fun to read!

Common Mistakes with Adverbs
Sometimes, students get confused between adverbs and adjectives. Remember, adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, while adjectives modify nouns.
For example:
- Correct: She sings beautifully. (Adverb modifying the verb “sings”)
- Incorrect: She is a beautiful singer. (Here, “beautiful” is an adjective modifying the noun “singer.”)
Another common mistake is putting the adverb in the wrong place in a sentence. For example, in the sentence ‘She quickly sings,’ the adverb ‘quickly‘ correctly describes how she sings.
Conclusion
Knowing what an adverb is and how it works is important for learning English. It helps us add detail and clarity to our sentences, making our speech and writing more vivid and expressive. With practice and the help of adverb worksheets for class 3, 4, and 5, you can become an expert at using adverbs in your sentences.
Next time you’re writing or reading, notice how adverbs help add more detail to actions, descriptions, or how much of something there is!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An adverb is a word that describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It provides more details like how, when, where, or to what extent an action happens.
Some examples of adverbs include words like “quickly,” “often,” “there,” and “very.” For example, in the sentence “She speaks softly,” the word “softly” is an adverb because it describes how she speaks.
To identify an adverb, ask yourself questions like: How is the action being done? When is it happening? Where is it happening? To what extent is it happening? Adverbs often end in “-ly,” but not always.
Yes, an adverb can modify an adjective to show the degree or intensity of something. For example, in the sentence “The movie was very exciting,” the adverb “very” modifies the adjective “exciting.”
Adverbs make language more descriptive and exciting. They help us provide more detail about actions, qualities, or other adverbs, making sentences clearer and more engaging.